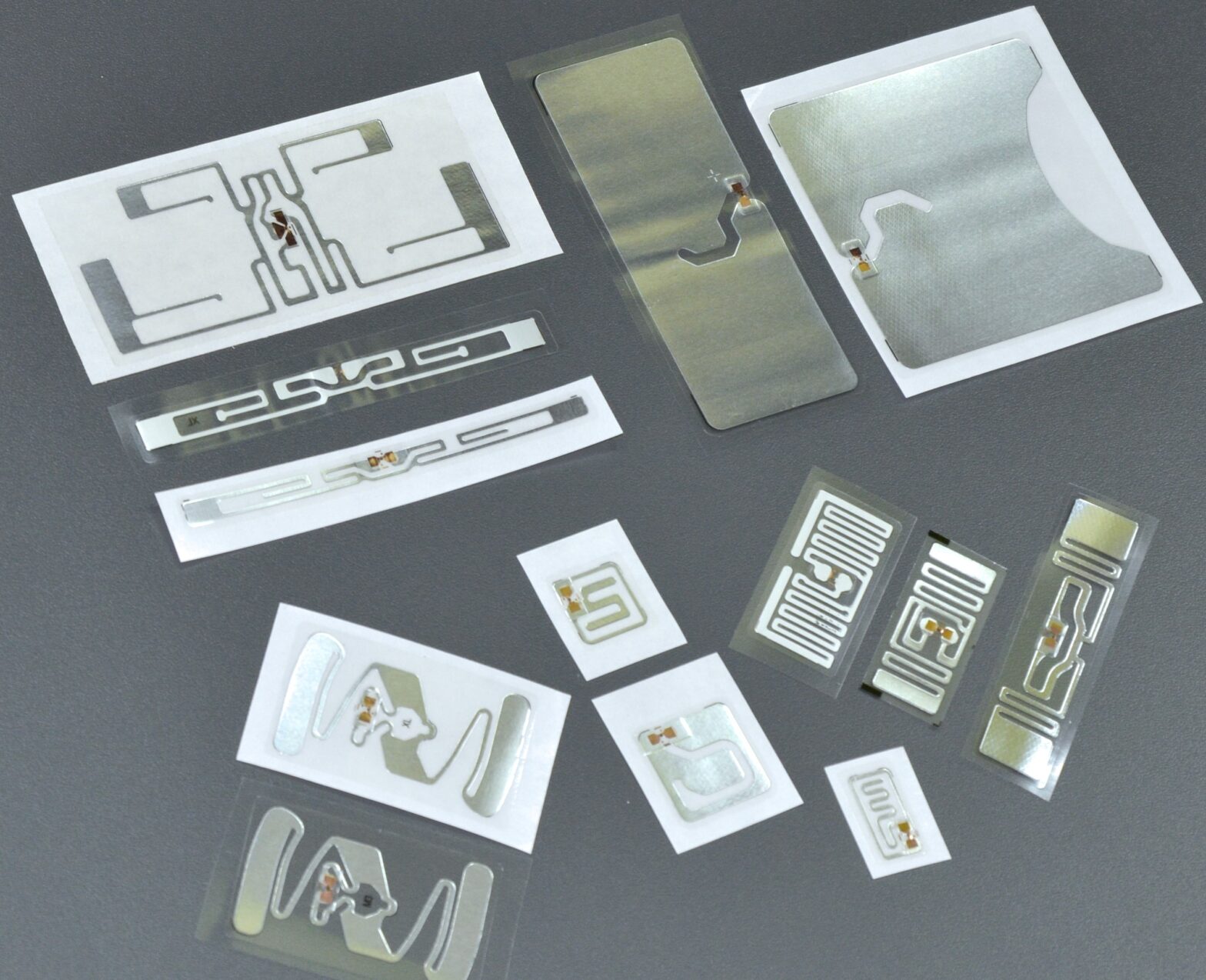
RFID label printers
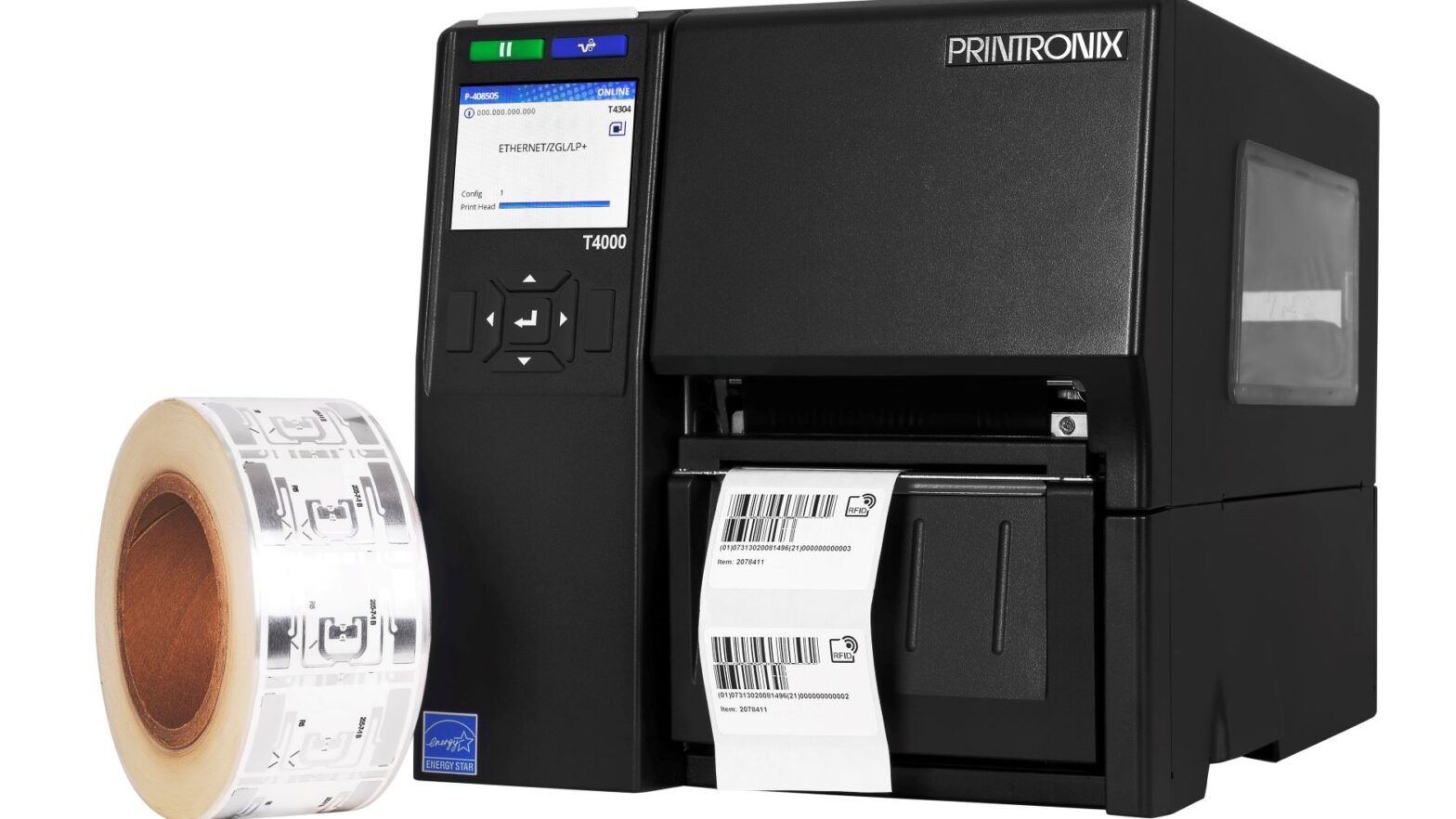
RFID label printers - RFID tag encoding can be conducted in many ways. Thermal transfer printers equipped with an RFID reader / coder are most often used for this purpose. RFID label printer makes simultaneous writing of information into RFID tags and printing data in the form of a code (...)